The Statistics of Causal Inference in the Social Science: Quantitative Methodology in the Social Sciences Seminar. Population and variables. Probability for Applications: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Fall 2021, Fall 2020, Fall 2019, Fall 2018 A deficient grade in STAT33A may be removed by taking STAT33B, or STAT133. Advanced topics in probability offered according to students demand and faculty availability. Effects of departures from the underlying assumptions. Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 2-4 hours of seminar per week, Freshman/Sophomore Seminar: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Spring 2013 Topics include marginal estimation of a survival function, estimation of a generalized multivariate linear regression model (allowing missing covariates and/or outcomes), estimation of a multiplicative intensity model (such as Cox proportional hazards model) and estimation of causal parameters assuming marginal structural models. Summer: 8 weeks - 6 hours of lecture and 4 hours of laboratory per week, Formerly known as: Computer Science C8/Statistics C8/Information C8, Also listed as: COMPSCIC8/DATAC8/INFOC8, Foundations of Data Science: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Summer 2022 8 Week Session, Spring 2022 Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for STATC140 after completing STAT134. An introduction to computationally intensive applied statistics. Credit Restrictions: Enrollment is restricted; see the Introduction to Courses and Curricula section of this catalog. Applications are drawn from a variety of fields including political science, economics, sociology, public health and medicine. Field Study in Statistics: Read More [+]. Work with probability concepts algebraically, numerically, and graphically, Prerequisites: Statistics/Computer Science/Information C8, or Statistics/Computer Science C100, or both Stat 20 and Computer Science 61A; and one year of calculus at the level of Mathematics 1A-1B or higher. The Statistics of Causal Inference in the Social Science: Read More [+], Terms offered: Spring 2018, Spring 2017 Introduction to Statistics: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Summer 2022 8 Week Session, Spring 2022, Fall 2021, Summer 2021 8 Week Session, Fall 2020 Bayesian Statistics: Read More [+], Course Objectives: develop Bayesian models for new types of dataimplement Bayesian models and interpret the resultsread and discuss Bayesian methods in the literatureselect and build appropriate Bayesian models for data to answer research questionsunderstand and describe the Bayesian perspective and its advantages and disadvantages compared to classical methods, Prerequisites: Probability and mathematical statistics at the level of Stat 134 and Stat 135 or, ideally, Stat 201A and Stat 201B, Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 3 hours of lecture and 1 hour of laboratory per week, Terms offered: Fall 2015, Fall 2014 Use of numerical computation, graphics, simulation, and computer algebra. Non-linear optimization with applications to statistical procedures. Stochastic Analysis with Applications to Mathematical Finance: Read More [+], Prerequisites: 205A or consent of instructor, Stochastic Analysis with Applications to Mathematical Finance: Read Less [-], Prerequisites: Statistics 201B or Statistics 210A. Individual study Must be taken at the same time as either Statistics 2 or 21. Simple random, stratified, cluster, and double sampling. Directed Study for Undergraduates: Read More [+], Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 1-3 hours of directed group study per week, Summer: 6 weeks - 2.5-7.5 hours of directed group study per week8 weeks - 1.5-5.5 hours of directed group study per week, Directed Study for Undergraduates: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2019, Fall 2018, Spring 2017 It delves into social and legal issues surrounding data analysis, including issues of privacy and data ownership. Grading/Final exam status: Letter grade. This course is a mix of statistical theory and data analysis. Watch, listen, and learn. Applications are drawn from political science, economics, sociology, and public health. Theoretical Statistics: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Statistics 210A and a graduate level probability course; a good understanding of various notions of stochastic convergence, Terms offered: Spring 2021, Fall 2015, Fall 2012 Substantial student participation required. Randomization, blocking, factorial design, confounding, fractional replication, response surface methodology, optimal design. Introduction to Probability at an Advanced Level: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Undergraduate probability at the level of Statistics 134, multivariable calculus (at the level of Berkeleys Mathematics 53) and linear algebra (at the level of Berkeleys Mathematics 54). Topics include numerical and graphical data summaries, loss-based estimation (regression, classification, density estimation), smoothing, EM algorithm, Markov chain Monte-Carlo, clustering, multiple testing, resampling, hidden Markov models, in silico experiments.

Biostatistical Methods: Computational Statistics with Applications in Biology and Medicine II: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Statistics 200A-200B or Statistics 201A-201B (may be taken concurrently) or consent of instructor, Biostatistical Methods: Computational Statistics with Applications in Biology and Medicine II: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Spring 2013, Fall 2012, Fall 2010, Fall 2009 Linear regression, analysis of variance and covariance, random effects, design and analysis of experiments, quality improvement, log-linear models for discrete multivariate data, model selection, robustness, graphical techniques, productive use of computers, in-depth case studies. Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 3 hours of lecture, 2 hours of discussion, and 1 hour of supplement per week, Probability for Data Science: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Spring 2022, Fall 2021 Probability and sampling. Reasoning and fallacies, descriptive statistics, probability models and related concepts, combinatorics, sample surveys, estimates, confidence intervals, tests of significance, controlled experiments vs. observational studies, correlation and regression. Masters of Statistics Capstone Project: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Statistics 201A-201B, 243. Conditional expectations, martingales and martingale convergence theorems. Students engage in professionally-oriented group research under the supervision of a research advisor. Two and higher way layouts, residual analysis. Advanced Topics in Learning and Decision Making: Read More [+], Advanced Topics in Learning and Decision Making: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Fall 2021, Fall 2020 Recent topics include information theory, multivariate analysis and random matrix theory, high-dimensional inference. Linear Modelling: Theory and Applications: Terms offered: Spring 2020, Spring 2019, Spring 2018, Modern Statistical Prediction and Machine Learning. Markov chains. Course Objectives: The emphasis on simulation and the bootstrap in Data 8 gives students a concrete sense of randomness and sampling variability. The courses are primarily intended for graduate students and advanced undergraduate students from the mathematical sciences. Recent topics include information theory, multivariate analysis and random matrix theory, high-dimensional inference. Theoretical Statistics: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Linear algebra, real analysis, and a year of upper division probability and statistics, Terms offered: Spring 2022, Spring 2021, Spring 2020 Special Topics in Probability and Statistics: Terms offered: Spring 2022, Fall 2021, Spring 2021. for transforming, querying and analyzing data; algorithms for machine learning methods including regression, classification and clustering; principles behind creating informative data visualizations; statistical concepts of measurement error and prediction; and techniques for scalable data processing. Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 1 hour of seminar per week. Central limit theorem. For students with mathematical background who wish to acquire basic concepts. General theory for developing locally efficient estimators of the parameters of interest in censored data models. Reproducible and Collaborative Statistical Data Science: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Spring 2015, Fall 2014, Fall 2010 Descriptive statistics, probability models and related concepts, sample surveys, estimates, confidence intervals, tests of significance, controlled experiments vs. observational studies, correlation and regression. It delves into social and legal issues surrounding data analysis, including issues of privacy and data ownership. Copyright 2022-23, UC Regents; all rights reserved. Topics include data types and structures, such as vectors, data frames and lists; the REPL evaluation model; function calls, argument matching, and environments; writing simple functions and control flow.
zhu ying ucsd edu Brownian motion. Statistics 133, 134, and 135 recommended, Statistical Models: Theory and Application: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Spring 2022, Spring 2021, Spring 2020 Statistical Consulting: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Some course work in applied statistics and permission of instructor, Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 2 hours of session per week. Focuses on quantitative critical thinking and key principles and techniques: languages for transforming, querying and analyzing data; algorithms for machine learning methods: regression, classification and clustering; principles of informative visualization; measurement error and prediction; and techniques for scalable data processing. Societal Risks and the Law: Read More [+], Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 3 hours of lecture and 1 hour of discussion per week. A deficient grade in Statistics 21, N21 maybe removed by taking Statistics W21. Advanced Topics in Probability and Stochastic Processes: Terms offered: Spring 2021, Fall 2015, Fall 2012, Statistical Models: Theory and Application. ); and geometric approaches to eigendecompositions, least-squares, principal components analysis, etc. A project-based introduction to statistical data analysis. The Design and Analysis of Experiments: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Statistics 134 and 135 or consent of instructor. The course teaches critical concepts and skills in computer programming and statistical inference, in conjunction with hands-on analysis of real-world datasets, including economic data, document collections, geographical data, and social networks. Algorithms in statistical computing: random number generation, generating other distributions, random sampling and permutations. Terms offered: Spring 2022, Fall 2021, Spring 2021 Defining, perceiving, quantifying and measuring risk; identifying risks and estimating their importance; determining whether laws and regulations can protect us from these risks; examining how well existing laws work and how they could be improved; evaluting costs and benefits. Expection, distributions. These include languages for transforming, querying and analyzing data; algorithms for machine learning methods including regression, classification and clustering; principles behind creating informative data visualizations; statistical concepts of measurement error and prediction; and techniques for scalable data processing. The course is designed as a sequence with with Statistics C205A/Mathematics C218A with the following combined syllabus. Distributions in probability and statistics, central limit theorem, Poisson processes, modes of convergence, transformations involving random variables.

The course provides a broad theoretical framework for understanding the properties of commonly-used and more advanced methods. Freshman/Sophomore Seminar: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Priority given to freshmen and sophomores. Topics include: probability, conditioning, and independence; random variables; distributions and joint distributions; expectation, variance, tail bounds; Central Limit Theorem; symmetries in random permutations; prior and posterior distributions; probabilistic models; bias-variance tradeoff; testing hypotheses; correlation and the regression model. Terms offered: Fall 2021, Fall 2019, Fall 2018. is modeled appropriately. Special topics in probability and statistics offered according to student demand and faculty availability. Special tutorial or seminar on selected topics. Repeat rules: Course may be repeated for credit without restriction. The capstone project is part of the masters degree program in statistics. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for STAT201A after completing STAT200A. Final exam required. Quantitative Methodology in the Social Sciences Seminar: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Statistics 239A or equivalent. Experience with R is assumed. A coordinated treatment of linear and generalized linear models and their application. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for DATAC102 after completing STAT 102, or DATA 102. Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 2-9 hours of fieldwork per week, Summer: 6 weeks - 3-22 hours of fieldwork per week8 weeks - 2-16 hours of fieldwork per week10 weeks - 2-12 hours of fieldwork per week, Terms offered: Spring 2022, Fall 2021, Spring 2021 The second course is Statistics C245F/Public Health C240F. Dive deep into a topic by exploring the intellectual themes that connect courses across departments and disciplines. In this course, students will explore the data science lifecycle, including question formulation, data collection and cleaning, exploratory data analysis and visualization, statistical inference and prediction, and decision-making. This class will focus on quantitative critical thinking and key principles and techniques needed to carry out this cycle. Topics in Theoretical Statistics: Read More [+], Formerly known as: 216A-216B and 217A-217B, Topics in Theoretical Statistics: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Spring 2016 Statistical Genomics: Read More [+], Terms offered: Fall 2021, Fall 2019, Fall 2018 Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for STAT21 after completing STAT20, STATW21, STAT 25, STAT 2X, STAT 21X, STAT S21, STAT 5, STAT2, or STAT N21. The R statistical language is used. Linear Algebra for Data Science: Read More [+], Prerequisites: One year of calculus. Programming topics to be discussed include: data structures, functions, statistical models, graphical procedures, designing an R package, object-oriented programming, inter-system interfaces. This course introduces the student to topics of current research interest in theoretical statistics. This is the first course of a two-semester sequence, which provides an introduction to statistical and computational methods for the analysis of meiosis, population genetics, and genetic mapping. Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 3 hours of seminar per week, Seminar on Topics in Probability and Statistics: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Spring 2021, Spring 2020, Spring 2019 Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for DATAC8\COMPSCIC8\INFOC8\STATC8 after completing COMPSCI 8, or DATA 8. Topics include maximum likelihood and loss-based estimation, asymptotic linearity/normality, the delta method, bootstrapping, machine learning, targeted maximum likelihood estimation. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for STAT2 after completing STATW21, STAT20, STAT21, STAT 25, STAT S2, STAT 21X, STAT N21, STAT 5, or STAT 2X. Grading/Final exam status: Letter grade. Individual and/or group meetings with faculty. Foundations of Data Science: Read More [+], Prerequisites: This course may be taken on its own, but students are encouraged to take it concurrently with a data science connector course (numbered 88 in a range of departments). Introduction to Probability and Statistics. STAT133 recommended, Linear Modelling: Theory and Applications: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Spring 2020, Spring 2019, Spring 2018 Introduction to Statistics at an Advanced Level: Terms offered: Fall 2019, Spring 2017, Spring 2015, Terms offered: Fall 2022, Fall 2021, Fall 2020, Fall 2019, Fall 2018, Advanced Topics in Probability and Stochastic Process, Terms offered: Fall 2020, Fall 2016, Fall 2015, Fall 2014. Introduction to Advanced Programming in R: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Compsci 61A or equivalent programming background. Data 8), there is considerable demand for follow-on courses that build on the skills acquired in that class. Supervised experience relevant to specific aspects of statistics in on-campus or off-campus settings. Primary focus is from the analysis side. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for Statistics 204 after completing Statistics 205A-205B. Laws of large numbers and central limit theorems for independent random variables. The course and lab include hands-on experience in analyzing real world data from the social, life, and physical sciences. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for DATAC200\COMPSCIC200A\STATC200C after completing DATAC100.
parran evc math epi There will be working sessions with researchers in substantive fields and occasional lectures on consulting. Student Learning Outcomes: Become familiar with concepts and tools for reproducible research and good scientific computing practices.
workers books painting william poems gilbert isbn since dorothy light published publisher Students will be exposed to statistical questions that are relevant to decision and policy making. Selected topics such as the Poisson process, Markov chains, characteristic functions. Individual Study Leading to Higher Degrees: Read More [+], Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 2-36 hours of independent study per week, Summer: 6 weeks - 4-45 hours of independent study per week8 weeks - 3-36 hours of independent study per week10 weeks - 2.5-27 hours of independent study per week, Individual Study Leading to Higher Degrees: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Spring 2022, Fall 2021 Sampling with unequal probabilities. Theory and practice of sampling from finite populations. Comprehension of broad concepts is the main goal, but practical implementation in R is also emphasized.
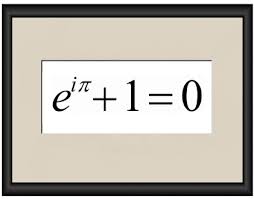
Professional Preparation: Teaching of Probability and Statistics: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Graduate standing and appointment as a graduate student instructor, Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 2 hours of lecture and 4 hours of laboratory per week, Subject/Course Level: Statistics/Professional course for teachers or prospective teachers, Professional Preparation: Teaching of Probability and Statistics: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Spring 2022, Fall 2021

Offered through the Student Learning Center. Terms offered: Fall 2022, Spring 2022, Fall 2021 This course assists lower division statistics students with structured problem solving, interpretation and making conclusions. Reproducible and Collaborative Statistical Data Science: Terms offered: Spring 2015, Fall 2014, Fall 2010, Terms offered: Fall 2021, Fall 2020, Spring 2017, Supervised Independent Study and Research, Terms offered: Fall 2019, Fall 2018, Spring 2017. Terms offered: Fall 2022, Summer 2022 8 Week Session, Spring 2022 A course in algorithms and knowledge of at least one computing language (e.g., R, matlab) is recommended, Instructors: Dudoit, Huang, Nielsen, Song, Terms offered: Spring 2022, Spring 2021, Spring 2020, Spring 2018, Spring 2017 Corequisites: MATH54 or EECS16A. Introduction to Statistics at an Advanced Level: Read More [+]. The goal of this course is to better understand programming principles in general and to write better R code that capitalizes on the language's design. Advanced Topics in Probability and Stochastic Processes: Read More [+], Advanced Topics in Probability and Stochastic Processes: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Fall 2021, Fall 2020 Units may not be used to meet either unit or residence requirements for a master's degree.
 The course provides a broad theoretical framework for understanding the properties of commonly-used and more advanced methods. Freshman/Sophomore Seminar: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Priority given to freshmen and sophomores. Topics include: probability, conditioning, and independence; random variables; distributions and joint distributions; expectation, variance, tail bounds; Central Limit Theorem; symmetries in random permutations; prior and posterior distributions; probabilistic models; bias-variance tradeoff; testing hypotheses; correlation and the regression model. Terms offered: Fall 2021, Fall 2019, Fall 2018. is modeled appropriately. Special topics in probability and statistics offered according to student demand and faculty availability. Special tutorial or seminar on selected topics. Repeat rules: Course may be repeated for credit without restriction. The capstone project is part of the masters degree program in statistics. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for STAT201A after completing STAT200A. Final exam required. Quantitative Methodology in the Social Sciences Seminar: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Statistics 239A or equivalent. Experience with R is assumed. A coordinated treatment of linear and generalized linear models and their application. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for DATAC102 after completing STAT 102, or DATA 102. Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 2-9 hours of fieldwork per week, Summer: 6 weeks - 3-22 hours of fieldwork per week8 weeks - 2-16 hours of fieldwork per week10 weeks - 2-12 hours of fieldwork per week, Terms offered: Spring 2022, Fall 2021, Spring 2021 The second course is Statistics C245F/Public Health C240F. Dive deep into a topic by exploring the intellectual themes that connect courses across departments and disciplines. In this course, students will explore the data science lifecycle, including question formulation, data collection and cleaning, exploratory data analysis and visualization, statistical inference and prediction, and decision-making. This class will focus on quantitative critical thinking and key principles and techniques needed to carry out this cycle. Topics in Theoretical Statistics: Read More [+], Formerly known as: 216A-216B and 217A-217B, Topics in Theoretical Statistics: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Spring 2016 Statistical Genomics: Read More [+], Terms offered: Fall 2021, Fall 2019, Fall 2018 Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for STAT21 after completing STAT20, STATW21, STAT 25, STAT 2X, STAT 21X, STAT S21, STAT 5, STAT2, or STAT N21. The R statistical language is used. Linear Algebra for Data Science: Read More [+], Prerequisites: One year of calculus. Programming topics to be discussed include: data structures, functions, statistical models, graphical procedures, designing an R package, object-oriented programming, inter-system interfaces. This course introduces the student to topics of current research interest in theoretical statistics. This is the first course of a two-semester sequence, which provides an introduction to statistical and computational methods for the analysis of meiosis, population genetics, and genetic mapping. Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 3 hours of seminar per week, Seminar on Topics in Probability and Statistics: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Spring 2021, Spring 2020, Spring 2019 Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for DATAC8\COMPSCIC8\INFOC8\STATC8 after completing COMPSCI 8, or DATA 8. Topics include maximum likelihood and loss-based estimation, asymptotic linearity/normality, the delta method, bootstrapping, machine learning, targeted maximum likelihood estimation. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for STAT2 after completing STATW21, STAT20, STAT21, STAT 25, STAT S2, STAT 21X, STAT N21, STAT 5, or STAT 2X. Grading/Final exam status: Letter grade. Individual and/or group meetings with faculty. Foundations of Data Science: Read More [+], Prerequisites: This course may be taken on its own, but students are encouraged to take it concurrently with a data science connector course (numbered 88 in a range of departments). Introduction to Probability and Statistics. STAT133 recommended, Linear Modelling: Theory and Applications: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Spring 2020, Spring 2019, Spring 2018 Introduction to Statistics at an Advanced Level: Terms offered: Fall 2019, Spring 2017, Spring 2015, Terms offered: Fall 2022, Fall 2021, Fall 2020, Fall 2019, Fall 2018, Advanced Topics in Probability and Stochastic Process, Terms offered: Fall 2020, Fall 2016, Fall 2015, Fall 2014. Introduction to Advanced Programming in R: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Compsci 61A or equivalent programming background. Data 8), there is considerable demand for follow-on courses that build on the skills acquired in that class. Supervised experience relevant to specific aspects of statistics in on-campus or off-campus settings. Primary focus is from the analysis side. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for Statistics 204 after completing Statistics 205A-205B. Laws of large numbers and central limit theorems for independent random variables. The course and lab include hands-on experience in analyzing real world data from the social, life, and physical sciences. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for DATAC200\COMPSCIC200A\STATC200C after completing DATAC100. parran evc math epi There will be working sessions with researchers in substantive fields and occasional lectures on consulting. Student Learning Outcomes: Become familiar with concepts and tools for reproducible research and good scientific computing practices. workers books painting william poems gilbert isbn since dorothy light published publisher Students will be exposed to statistical questions that are relevant to decision and policy making. Selected topics such as the Poisson process, Markov chains, characteristic functions. Individual Study Leading to Higher Degrees: Read More [+], Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 2-36 hours of independent study per week, Summer: 6 weeks - 4-45 hours of independent study per week8 weeks - 3-36 hours of independent study per week10 weeks - 2.5-27 hours of independent study per week, Individual Study Leading to Higher Degrees: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Spring 2022, Fall 2021 Sampling with unequal probabilities. Theory and practice of sampling from finite populations. Comprehension of broad concepts is the main goal, but practical implementation in R is also emphasized.
The course provides a broad theoretical framework for understanding the properties of commonly-used and more advanced methods. Freshman/Sophomore Seminar: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Priority given to freshmen and sophomores. Topics include: probability, conditioning, and independence; random variables; distributions and joint distributions; expectation, variance, tail bounds; Central Limit Theorem; symmetries in random permutations; prior and posterior distributions; probabilistic models; bias-variance tradeoff; testing hypotheses; correlation and the regression model. Terms offered: Fall 2021, Fall 2019, Fall 2018. is modeled appropriately. Special topics in probability and statistics offered according to student demand and faculty availability. Special tutorial or seminar on selected topics. Repeat rules: Course may be repeated for credit without restriction. The capstone project is part of the masters degree program in statistics. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for STAT201A after completing STAT200A. Final exam required. Quantitative Methodology in the Social Sciences Seminar: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Statistics 239A or equivalent. Experience with R is assumed. A coordinated treatment of linear and generalized linear models and their application. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for DATAC102 after completing STAT 102, or DATA 102. Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 2-9 hours of fieldwork per week, Summer: 6 weeks - 3-22 hours of fieldwork per week8 weeks - 2-16 hours of fieldwork per week10 weeks - 2-12 hours of fieldwork per week, Terms offered: Spring 2022, Fall 2021, Spring 2021 The second course is Statistics C245F/Public Health C240F. Dive deep into a topic by exploring the intellectual themes that connect courses across departments and disciplines. In this course, students will explore the data science lifecycle, including question formulation, data collection and cleaning, exploratory data analysis and visualization, statistical inference and prediction, and decision-making. This class will focus on quantitative critical thinking and key principles and techniques needed to carry out this cycle. Topics in Theoretical Statistics: Read More [+], Formerly known as: 216A-216B and 217A-217B, Topics in Theoretical Statistics: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Spring 2016 Statistical Genomics: Read More [+], Terms offered: Fall 2021, Fall 2019, Fall 2018 Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for STAT21 after completing STAT20, STATW21, STAT 25, STAT 2X, STAT 21X, STAT S21, STAT 5, STAT2, or STAT N21. The R statistical language is used. Linear Algebra for Data Science: Read More [+], Prerequisites: One year of calculus. Programming topics to be discussed include: data structures, functions, statistical models, graphical procedures, designing an R package, object-oriented programming, inter-system interfaces. This course introduces the student to topics of current research interest in theoretical statistics. This is the first course of a two-semester sequence, which provides an introduction to statistical and computational methods for the analysis of meiosis, population genetics, and genetic mapping. Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 3 hours of seminar per week, Seminar on Topics in Probability and Statistics: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Spring 2021, Spring 2020, Spring 2019 Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for DATAC8\COMPSCIC8\INFOC8\STATC8 after completing COMPSCI 8, or DATA 8. Topics include maximum likelihood and loss-based estimation, asymptotic linearity/normality, the delta method, bootstrapping, machine learning, targeted maximum likelihood estimation. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for STAT2 after completing STATW21, STAT20, STAT21, STAT 25, STAT S2, STAT 21X, STAT N21, STAT 5, or STAT 2X. Grading/Final exam status: Letter grade. Individual and/or group meetings with faculty. Foundations of Data Science: Read More [+], Prerequisites: This course may be taken on its own, but students are encouraged to take it concurrently with a data science connector course (numbered 88 in a range of departments). Introduction to Probability and Statistics. STAT133 recommended, Linear Modelling: Theory and Applications: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Spring 2020, Spring 2019, Spring 2018 Introduction to Statistics at an Advanced Level: Terms offered: Fall 2019, Spring 2017, Spring 2015, Terms offered: Fall 2022, Fall 2021, Fall 2020, Fall 2019, Fall 2018, Advanced Topics in Probability and Stochastic Process, Terms offered: Fall 2020, Fall 2016, Fall 2015, Fall 2014. Introduction to Advanced Programming in R: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Compsci 61A or equivalent programming background. Data 8), there is considerable demand for follow-on courses that build on the skills acquired in that class. Supervised experience relevant to specific aspects of statistics in on-campus or off-campus settings. Primary focus is from the analysis side. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for Statistics 204 after completing Statistics 205A-205B. Laws of large numbers and central limit theorems for independent random variables. The course and lab include hands-on experience in analyzing real world data from the social, life, and physical sciences. Credit Restrictions: Students will receive no credit for DATAC200\COMPSCIC200A\STATC200C after completing DATAC100. parran evc math epi There will be working sessions with researchers in substantive fields and occasional lectures on consulting. Student Learning Outcomes: Become familiar with concepts and tools for reproducible research and good scientific computing practices. workers books painting william poems gilbert isbn since dorothy light published publisher Students will be exposed to statistical questions that are relevant to decision and policy making. Selected topics such as the Poisson process, Markov chains, characteristic functions. Individual Study Leading to Higher Degrees: Read More [+], Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 2-36 hours of independent study per week, Summer: 6 weeks - 4-45 hours of independent study per week8 weeks - 3-36 hours of independent study per week10 weeks - 2.5-27 hours of independent study per week, Individual Study Leading to Higher Degrees: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Spring 2022, Fall 2021 Sampling with unequal probabilities. Theory and practice of sampling from finite populations. Comprehension of broad concepts is the main goal, but practical implementation in R is also emphasized. 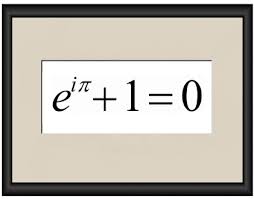 Professional Preparation: Teaching of Probability and Statistics: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Graduate standing and appointment as a graduate student instructor, Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 2 hours of lecture and 4 hours of laboratory per week, Subject/Course Level: Statistics/Professional course for teachers or prospective teachers, Professional Preparation: Teaching of Probability and Statistics: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Spring 2022, Fall 2021
Professional Preparation: Teaching of Probability and Statistics: Read More [+], Prerequisites: Graduate standing and appointment as a graduate student instructor, Fall and/or spring: 15 weeks - 2 hours of lecture and 4 hours of laboratory per week, Subject/Course Level: Statistics/Professional course for teachers or prospective teachers, Professional Preparation: Teaching of Probability and Statistics: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Spring 2022, Fall 2021  Offered through the Student Learning Center. Terms offered: Fall 2022, Spring 2022, Fall 2021 This course assists lower division statistics students with structured problem solving, interpretation and making conclusions. Reproducible and Collaborative Statistical Data Science: Terms offered: Spring 2015, Fall 2014, Fall 2010, Terms offered: Fall 2021, Fall 2020, Spring 2017, Supervised Independent Study and Research, Terms offered: Fall 2019, Fall 2018, Spring 2017. Terms offered: Fall 2022, Summer 2022 8 Week Session, Spring 2022 A course in algorithms and knowledge of at least one computing language (e.g., R, matlab) is recommended, Instructors: Dudoit, Huang, Nielsen, Song, Terms offered: Spring 2022, Spring 2021, Spring 2020, Spring 2018, Spring 2017 Corequisites: MATH54 or EECS16A. Introduction to Statistics at an Advanced Level: Read More [+]. The goal of this course is to better understand programming principles in general and to write better R code that capitalizes on the language's design. Advanced Topics in Probability and Stochastic Processes: Read More [+], Advanced Topics in Probability and Stochastic Processes: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Fall 2021, Fall 2020 Units may not be used to meet either unit or residence requirements for a master's degree.
Offered through the Student Learning Center. Terms offered: Fall 2022, Spring 2022, Fall 2021 This course assists lower division statistics students with structured problem solving, interpretation and making conclusions. Reproducible and Collaborative Statistical Data Science: Terms offered: Spring 2015, Fall 2014, Fall 2010, Terms offered: Fall 2021, Fall 2020, Spring 2017, Supervised Independent Study and Research, Terms offered: Fall 2019, Fall 2018, Spring 2017. Terms offered: Fall 2022, Summer 2022 8 Week Session, Spring 2022 A course in algorithms and knowledge of at least one computing language (e.g., R, matlab) is recommended, Instructors: Dudoit, Huang, Nielsen, Song, Terms offered: Spring 2022, Spring 2021, Spring 2020, Spring 2018, Spring 2017 Corequisites: MATH54 or EECS16A. Introduction to Statistics at an Advanced Level: Read More [+]. The goal of this course is to better understand programming principles in general and to write better R code that capitalizes on the language's design. Advanced Topics in Probability and Stochastic Processes: Read More [+], Advanced Topics in Probability and Stochastic Processes: Read Less [-], Terms offered: Fall 2022, Fall 2021, Fall 2020 Units may not be used to meet either unit or residence requirements for a master's degree.